Kuali Communities Overview
As an introduction to the Kuali Financial System (KFS) and its documentation, it is important that you understand how KFS is a part of a larger community.
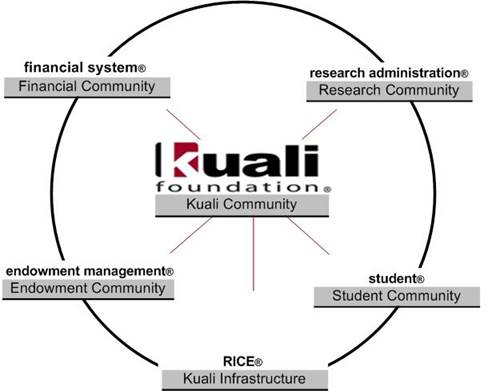
The KFS is a higher-education, community-source software project that is merely a spoke in the wheel of the larger Kuali Community. The Kuali Community is the hub of a wheel of a growing number of communities, each of which are made up of people and functions. Together they are creating a comprehensive suite of open, modular and distributed administrative software systems that combine the proven functionality of legacy applications with the ease and universality of online services. The Kuali Foundation serves all of these communities and assumes specific responsibilities related to keeping the wheel in motion.
Each individual community shares a similar organizational structure and some modular functionality while its components stand alone to perform unique functions. All of these communities are designed for seamless integration with each other, yet each project is made up of modules that provide a variety of implementation combinations to suit any Carnegie-class institution's unique business needs.
Kuali communities overview
|
Community |
Name |
Personnel |
Functions |
|
Kuali Community |
Kuali Foundation (KF) |
Board of Directors, Partner Institutions, Commercial Affiliates, Technical Council |
Collaboration infrastructure, copyright holding, licensing, resource planning, licensing, documentation, bug tracking, legal services, user support |
|
Financial Community |
Kuali Financial System (KFS) |
Project Board, Project Management, Functional Council, Development Teams, Subject Matter Experts |
Financial transactions, General Ledger, Chart of Accounts, reporting/decision support, contracts & grants, vendor, purchasing/accounts payable, labor distribution, effort certification, budget, accounts receivable, capital assets |
|
Research Community |
Kuali Research Administration (KRA) |
Project Board, Project Management, Functional Council, Development Teams, Subject Matter Experts |
Proposal development, budget development, routing form, grants.gov integration, institutional review board (IRB) / human subjects, awards, conflict of interest |
|
Kuali Infrastructure Community |
Kuali Rice (KR) |
Development Team |
Kuali Nervous System (KNS), Kuali Service Bus (KSB), Kuali Enterprise Notification (KEN), Kuali Enterprise Workflow (KEW), Kuali Identify Management (KIM) |
|
Endowment Community |
Kuali Endowment Management ( KEM) |
Project Board, Project Management, Functional Council, Development Teams, Subject Matter Experts |
Investment tracking & reporting, investment participation (endowment and non-endowment) Management and reporting, including unitized transaction, budgeted and actual income projections (pooled funds and separately invested holdings), access to donor instructions, manage available funds with searchable data elements describing the terms of use. |
|
Student Community |
Functional Steering Committee, Technical Steering Committee |
Person, time, learning unit, learning result, learning plan, learning resources, concierge |
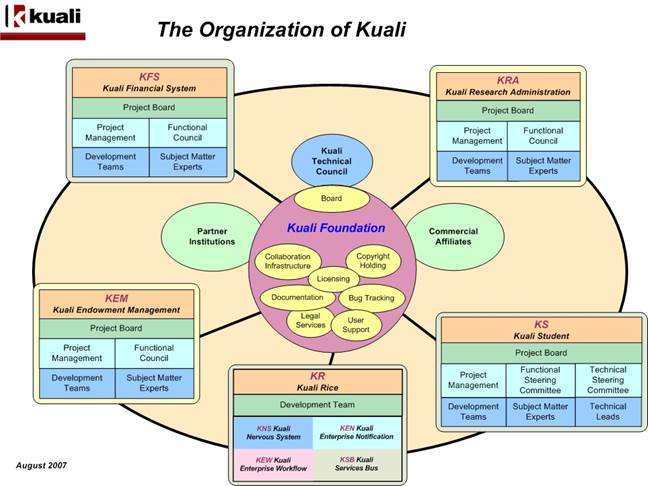
The following list provides a brief description of the major communities that make up the larger Kuali community:
• Kuali Foundation (KF): Employs staff to coordinate partner efforts and to manage and protect the Foundation's intellectual property. The Kuali Foundation manages a growing portfolio of enterprise software applications for colleges and universities. A lightweight Foundation staff coordinates the activities of Foundation members for critical software development and coordination activities such as source code control, release engineering, packaging, documentation, project management, software testing and quality assurance, conference planning, and educating and assisting members of the Kuali Partners Program.
• Kuali Partners Program (KPP): The Kuali Partners Program (KPP) is the means for organizations to get involved in the Kuali software community and influence its future through voting rights to determine software development priorities. Membership dues pay staff to perform quality assurance (QA) work, release engineering, packaging, documentation, and other work to coordinate the timely enhancement and release of quality software, and other services valuable to the members. Partners are also encouraged to tender functional, technical, support or administrative staff members to the Kuali Foundation for specific periods of time.
• Kuali Commercial Affiliates (KCA): A designation provided to commercial affiliates who become part of the Kuali Partners Program to provide for-fee guidance, support, implementation, and integration services related to the Kuali software. Affiliates hold no ownership of Kuali intellectual property, but are full KPP participants. Affiliates may provide packaged versions of Kuali that provide value for installation or integration beyond the basic Kuali software. Affiliates may also offer other types of training, documentation, or hosting services.
• Kuali Technical Council (KTC): Sets development standards and processes, ensures compliance with established standards and procedures among contributors. Responsible to the Kuali Foundation Board for the technical success of the project, the KTC is an operationally representative group of technical leaders who work with project managers and other operational leadership. The Council implements sustainable practices that ensure software quality by achieving an effective balance between sound architecture and the meeting of project deadlines and functional requirements.
• Project Boards: Provide management and oversight of the business and affairs of projects, including management of assets and resource allocation. The Board of Directors for a Kuali community project establishes and maintains the coordination processes needed to support the development and release of the Kuali software. Further, the project boards act as a 'court of final appeal' for discussions, work groups, and collaborative member activities of the project.
• Functional Councils: Provide overall project guidance related to the identification and prioritization of business practices and functional requirements developed by each software application project. Comprised of senior administrators from core Kuali institutions, members serve as primary functional subject matter experts who communicate functional specifications to development teams.
• Kuali Rice (KR): Provides an enterprise-class middleware suite of integrated products that allow both Kuali and non-Kuali applications to be built in an agile fashion, such that developers can react to end-user business requirements efficiently and produce high-quality business applications. Based on Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) concepts, KR enables developers to build robust systems with common enterprise workflow functionality, customizable and configurable user interfaces with a clean and universal look and feel, and general notification features to allow for a consolidated list of work 'action items'. Together these functions provide a re-usable development framework that encourages a simplified approach to developing true business functionality as modular applications.
• Kuali Research Administration (KRA): Delivers a means to administer your institution's research information, improve access to this information, and enhance support for research compliance. Based on the functionality of MIT's Coeus system, KRA is a re-engineering effort that adheres to the Kuali Architecture and Standards while filling in missing functionality. The application includes Proposal & Budget Development, Routing Form, Grants.gov Integration, Institutional Review Board (IRB) / Human Subjects, Awards, Conflict of Interest, Institute Proposal / Negotiations, Report Tracking, Subcontracts, Cost Share Commitment Tracking, Animal Care and Use, Bio-Safety Management, Subrecipient Monitoring, Export Controls / ITAR Management, and Chemical Tracking System.
• Kuali Endowment Management (KEM): Provides functionality to manage and report endowment funds and charitable trusts. It captures information to track endowment funds (including security information, investment activity records, actual asset allocations, and investment pool data). It also tracks and records investment performance (investment income, realized gains and losses, unrealized gains and losses, fees to the various funds, historical book value, accumulated earnings, and net gains, etc.). KEM also supports standard and ad hoc inquiries including balance inquiries for current and historical balances, balances by individual funds, and balances by security or other asset. Finally, it assists in managing investment pools via functionality that automates investment of donor funds in the institution's pooled or common funds, provides historical unit values and spending policy rates by pool, and projects the budgeted payout or the anticipated actual income for the current and subsequent fiscal year.
• Kuali Student (KS): Supports students and other users with a student-centric system that provides real-time, cost-effective, scalable support to help them identify and achieve their goals while simplifying or eliminating administrative tasks. The high-level entities include person (evolving roles-student, instructor, etc.), time (nested units of time - semesters, terms, classes), learning unit (assigned to any learning activity), learning result (grades, assessments, evaluations), learning plan (intentions, activities, major, degree), and learning resources (instructors, classrooms, equipment). The concierge function is a self-service information-sharing system that aligns information with needs and tasks to accomplish goals. Support for integration of locally-developed processes provides flexibility to accommodate any institution's needs.
Kuali Financial System (KFS): Delivers a comprehensive suite of functionality to serve the financial system needs of all Carnegie-Class institutions. An enhancement of the proven functionality of Indiana University's Financial Information System (FIS), KFS meets GASB and FASB standards while providing a strong control environment to keep pace with advances in both technology and business. Modules include financial transactions, General Ledger (GL), Chart of Accounts, reporting/decision support, post-award contract administration, purchasing/accounts payable, labor distribution, budget, accounts receivable and capital assets. A key component of the KFS is an 'electronic document' (e-doc) environment in which electronic documents are initiated on a personal computer, electronically routed through an approval process, and eventually passed to the General Ledger. KFS is important to those who use and process financial information for a variety of reasons. It reduces paper processes; enables faster turnaround and allows for decisions to be made based on up-to-date information; provides built-in checks and balances reducing mistakes and the need to correct errors; gives more control and management flexibility to documents; and creates audit trails.
 About the KFS User
Documentation
About the KFS User
Documentation